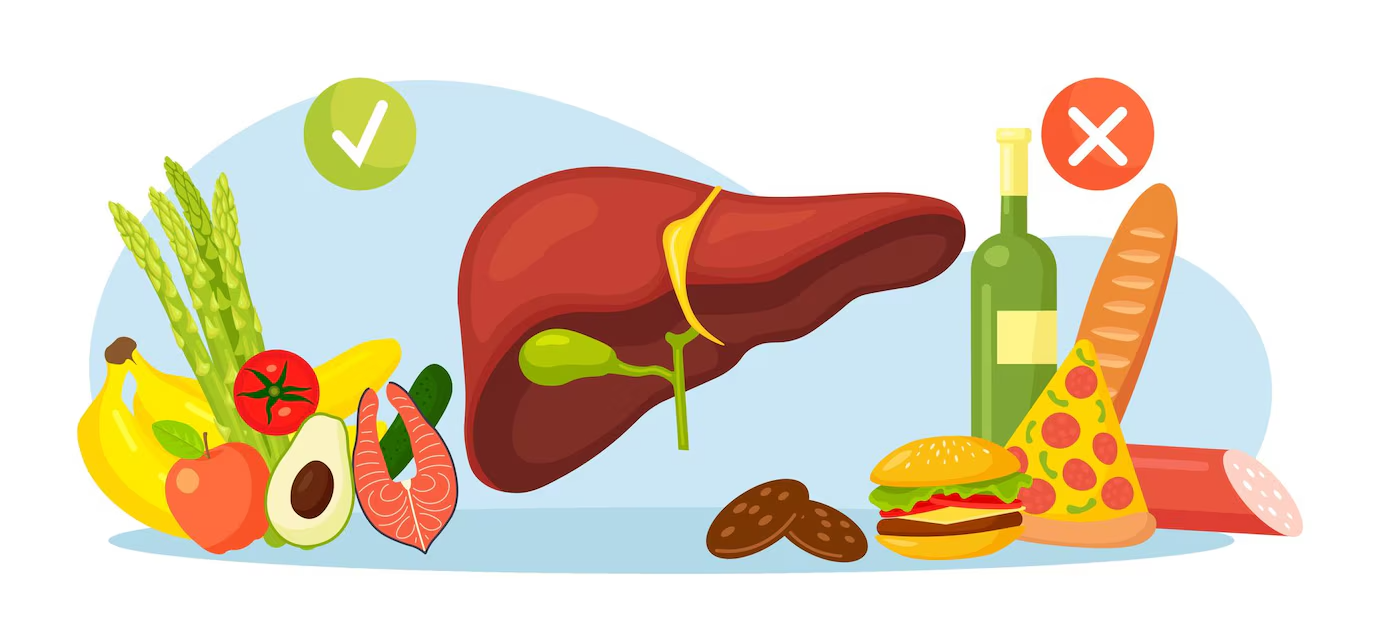
Fatty liver disease occurs when the liver stores an abnormal amount of fat, leading to potential impairment of liver function and increased risk of liver injury. Alcoholic fatty liver disease results from excessive alcohol consumption, causing the liver to produce harmful substances during alcohol breakdown that can damage liver cells and cause inflammation. Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is typically linked to dietary and lifestyle habits, commonly affecting individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, and those with excess weight or obesity. Due to the strong connection between fatty liver disease and metabolic health, some fatty liver diet modifications are often recommended. Currently, there are no established medical treatments for preventing or reversing fatty liver disease.
Maintaining a well-rounded diet rich in vibrant fruits, vegetables, whole grains packed with fiber, beneficial fats, lean proteins, and calcium sources is crucial for optimal liver function and overall health. Specific foods have shown exceptional potential in safeguarding against liver disease and enhancing outcomes for individuals with existing liver conditions. Here, we'll distinguish top-performing and bad food for the liver.
Garlic supplements have been found to have a positive effect on the metabolic profile of individuals with nonalcohol-related fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Including garlic in your fatty liver diet, either raw or cooked, may provide benefits for the liver.
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, sardines, walnuts, and flaxseed, have been associated with potential improvements in liver fat levels, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, and body mass index (BMI) in people with NAFLD.
Regular coffee consumption has been significantly associated with a decreased risk of liver fibrosis development in individuals diagnosed with NAFLD. It is an accessible beverage that may provide benefits beyond a burst of energy.
Research in mice with NAFLD has shown that broccoli can help the liver break down fats faster, potentially reducing their accumulation. Though further human studies are required, including broccoli in your fatty liver diet may support liver health.
Green tea provides antioxidants such as catechin, which have been suggested to improve the symptoms of fatty liver disease. This natural beverage has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years.
High in omega-3 fatty acids, walnuts are associated with a reduced risk of NAFLD. Including them in your diet can be a nutritious way to potentially support liver health.
Extra-virgin olive oil has been found to have several protective effects on the liver, including minimizing inflammation and insulin resistance. These benefits can aid in preventing or healing liver damage. Olive oil not only helps in quelling liver inflammation but also contributes to lowering inflammation throughout the body.
Including these best foods for fatty liver in your diet may help support the healing process.
When dealing with fatty liver disease, it's crucial to pay attention to the foods and drinks you consume to help manage the condition effectively. Here are some key foods and fruits to avoid for fatty liver individuals:
Alcohol is a major contributor to fatty liver disease, particularly alcoholic fatty liver disease, and can exacerbate liver damage. It's recommended to limit or completely avoid alcohol consumption to improve liver health.
Beverages high in sugar, such as soda and fruit juices with added sugars, can contribute to liver fat accumulation. Opt for water, herbal teas, or infused water with lemon or other fruits as healthier alternatives.
Consumption of red and processed meats has been linked to increased rates of liver fat deposits. Consider reducing your intake of red and processed meats and opt for lean proteins like poultry, fish, or plant-based protein sources.
Regular consumption of fast food, which is often high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and calories, can contribute to the development and progression of fatty liver disease. Try fast foods to avoid with fatty liver and focus on homemade, whole food meals rich in nutrients.
By minimizing or eliminating these foods and drinks from your diet, you can support your liver health and improve the management of fatty liver disease. Instead, focus on incorporating nutrient-dense, whole foods that are beneficial for your liver health, such as those mentioned in the best foods and drinks for a fatty liver diet.
Related: Healthy Smoothie Recipes for Liver Detox and Health